Sunbelt 2026 - Daytona Beach
Hilton Daytona Beach Oceanfront Resort
100 North Atlantic AvenueDaytona Beach, FL 32118-4204
United States
Sunbelt is INSNA's Annual Conference. The conference brings together researchers from around the globe to promote research and scholarship around social network analysis.
The 2026 conference will take place June 22 - 27 in Daytona Beach, Florida. Click the tabs above to learn more about the conference. We hope you'll join us at Sunbelt!
Chris McCarty, University of Florida (Chair)
H. Russell Bernard, University of Florida
John Skvoretz, University of South Florida
If you have any questions about Sunbelt 2026, please reach out to the INSNA Office directly at support@insna.org.
| Price | |
|---|---|
|
2026 Sunbelt Member Reg. (Includes banquet)
Registration Ends 5/18/26 at 11:59 PM EDT
|
$450.00 |
|
2026 Sunbelt Student Member (Includes Banquet)
Registration Ends 5/18/26 at 11:59 PM EDT
|
$250.00 |
|
2026 Sunbelt Student Non-Member (Includes Banquet)
Registration Ends 5/18/26 at 11:59 PM EDT
|
$350.00 |
|
2026 Sunbelt Non-Member (Includes Banquet)
Registration Ends 5/18/26 at 11:59 PM EDT
|
$650.00 |
| Price | |
|---|---|
|
2026 Sunbelt Member (Includes Banquet)
Registration Opens 5/19/26 at 12:00 AM EDT
|
$550.00 |
|
2026 Sunbelt Student Member (Includes Banquet)
Registration Opens 5/19/26 at 12:00 AM EDT
|
$300.00 |
|
2026 Sunbelt Non-Member (Includes Banquet)
Registration Opens 5/19/26 at 12:00 AM EDT
|
$750.00 |
|
2026 Sunbelt Student Non-Member (Includes Banquet)
Registration Opens 5/19/26 at 12:00 AM EDT
|
$400.00 |
| Price | |
|---|---|
|
Sunbelt 2026 Virtual - Student Member
Registration Ends 6/27/26 at 11:59 PM EDT
|
$100.00 |
|
Sunbelt 2026 Virtual - Member
Registration Ends 6/27/26 at 11:59 PM EDT
|
$200.00 |
|
Sunbelt 2026 Virtual - Non-Member
Registration Ends 6/27/26 at 11:59 PM EDT
|
$300.00 |
|
Sunbelt 2026 Virtual - Non-Member
Registration Ends 6/27/26 at 11:59 PM EDT
|
$300.00 |
| Price | |
|---|---|
|
2026 Sunbelt Member - Late (Includes Banquet)
Registration Opens 6/22/26 at 12:00 AM EDT
|
$650.00 |
|
2026 Sunbelt Student Mbr.-Late (Includes Banquet)
Registration Opens 6/22/26 at 12:00 AM EDT
|
$350.00 |
|
2026 Sunbelt Non-Member - Late (Includes Banquet)
Registration Opens 6/22/26 at 12:00 AM EDT
|
$850.00 |
|
2026 Student Non-Member - Late (Includes Banquet)
Registration Opens 6/22/26 at 12:00 AM EDT
|
$450.00 |
| Price | |
|---|---|
|
Egocentric Network Analysis with R
Raffaele Vacca Full Day |
$200.00 |
|
Large Language Models, Text Embeddings...
Ayan-Yue Gupta and Thomas Bryan Smith Full Day |
$200.00 |
|
Student - Egocentric Network Analysis with R
Raffaele Vacca Full Day |
$125.00 |
|
Student -Large Language Models, Text Embeddings...
Ayan-Yue Gupta and Thomas Bryan Smith Full Day |
$125.00 |
| Price | |
|---|---|
|
Micro-Macro Network Analysis Using Netmediate
Scott Duxbury Half Day |
$100.00 |
|
Student - Beyond APIs: Collecting Web Data for...
Pranav Goel, Scott Cambo, and David Lazer Half Day |
$75.00 |
|
Seeing Science Through Networks: Disciplinary...
Assemgul Kozhabek and Daniele Fanelli Half Day |
$100.00 |
|
Student - Micro-Macro Network Analysis Using...
Scott Duxbury Half Day |
$75.00 |
|
Beyond APIs: Collecting Web Data for Research...
Pranav Goel, Scott Cambo, and David Lazer Half Day |
$100.00 |
|
Student - Seeing Science Through Networks:...
Assemgul Kozhabek and Daniele Fanelli Half Day |
$75.00 |
|
Introduction to Relational Event Models
Melania Lembo Half Day |
$100.00 |
|
Student - Introduction to Relational Event Models
Melania Lembo, Martina Boschi, and Ernst C. Wit Half Day |
$75.00 |
| Price | |
|---|---|
|
Exponential Family Random Graph Modeling (ERGMs)..
Carter T. Butts and Pavel N. Krivitsky Half Day |
$100.00 |
|
An Introduction to the Design, Administration...
Michelle Birkett, Patrick Janulis, Gregory Phillips II, Bernie Hogan, Joshua Melville, and Kate Banner Half Day |
$100.00 |
|
Practical Tools for Surveying, Visualizing, and...
Sarah Galey-Horn and William Nicholas Bork Rodriguez Half Day |
$100.00 |
|
All You Need to Know About Relational...
Martina Boschi, Melania Lembo, Jürgen Lerner, and Ernst C. Wit Half Day |
$100.00 |
|
Student - Exponential Family Random Graph...
Carter T. Butts and Pavel N. Krivitsky Half Day |
$75.00 |
|
Student - An Introduction to the Design,...
Michelle Birkett, Patrick Janulis, Gregory Phillips II, Bernie Hogan, Joshua Melville, and Kate Banner Half Day |
$75.00 |
|
Student - Practical Tools for Surveying,...
Sarah Galey-Horn and William Nicholas Bork Rodriguez Half Day |
$75.00 |
|
Student - All You Need to Know About Relational...
Martina Boschi, Melania Lembo, Jürgen Lerner, and Ernst C. Wit Half Day |
$75.00 |
| Price | |
|---|---|
|
Mixed Methods Research into Social Networks
Elisa Bellotti Full Day |
$200.00 |
|
Socio-Semantic Network Analysis and Modelling
Nikita Basov Full Day |
$200.00 |
|
Student - Mixed Methods Research into Social...
Elisa Bellotti Full Day |
$125.00 |
|
Student - Socio-Semantic Network Analysis and...
Nikita Basov Full Day |
$125.00 |
| Price | |
|---|---|
|
Soccer Analytics
Ulrik Brandes and Gordana Marmulla Half Day |
$100.00 |
|
Mediation and Moderation Analysis in ERGM...
Scott Dubury and Jenna Wersching Half Day |
$100.00 |
|
Continuous Time Network Dynamics with Statnet
Carter T. Butts Half Day |
$100.00 |
|
Social Network Approaches for Behavior Change
Tom Valente Half Day |
$100.00 |
|
Student - Soccer Analytics
Ulrik Brandes and Gordana Marmulla Half Day |
$75.00 |
|
Student - Mediation and Moderation Analysis in...
Scott Dubury and Jenna Wersching Half Day |
$75.00 |
|
Student - Continuous Time Network Dynamics with...
Carter T. Butts Half Day |
$75.00 |
|
Student -Social Network Approaches for Behavior...
Tom Valente Half Day |
$75.00 |
| Price | |
|---|---|
|
FIFA World Cup Match Analysis Primer
Ulrik Brandes and Gordana Marmulla Half Day |
$100.00 |
|
Valued Network Modeling with Statnet
Pavel N. Krivitsky and Carter T. Butts Half Day |
$100.00 |
|
Artificial Intelligence for the Scientist in...
George G. Vega Yon Half Day |
$100.00 |
|
Student - FIFA World Cup Match Analysis...
Ulrik Brandes and Gordana Marmulla Half Day |
$75.00 |
|
Student - Valued Network Modeling with...
Pavel N. Krivitsky and Carter T. Butts Half Day |
$75.00 |
|
Student - Artificial Intelligence for the...
George G. Vega Yon Half Day |
$75.00 |
| Price | |
|---|---|
|
Understanding Diffusion with NetdiffuseR
George G. Vega Yon, Tom Valente, and Aníbal L. Olivera Morales Half Day |
$100.00 |
|
Fluctuating Opinions in Social Networks:...
Farhad Farokhi, Nicholas Kah Yean Low, Yutong Bu, Jarra Horstman, Andrew Melatos, Robin Evans, Yijun Chen, and Julian Greentree Half Day |
$100.00 |
|
Introduction to Core Social Network Concepts
Steve Borgatti and Rich DeJordy Half Day |
$100.00 |
|
A Comprehensive Regression Framework for...
Michael Schweinberger and Cornelius Fritz Half Day |
$100.00 |
|
Student - Understanding Diffusion with...
George G. Vega Yon, Tom Valente, and Aníbal L. Olivera Morales Half Day |
$75.00 |
|
Student - Fluctuating Opinions in Social...
Farhad Farokhi, Nicholas Kah Yean Low, Yutong Bu, Jarra Horstman, Andrew Melatos, Robin Evans, Yijun Chen, and Julian Greentree Half Day |
$75.00 |
|
Student - Introduction to Core Social Network...
Steve Borgatti and Rich DeJordy Half Day |
$75.00 |
|
Student - A Comprehensive Regression Framework...
Michael Schweinberger and Cornelius Fritz Half Day |
$75.00 |
| Price | |
|---|---|
|
Banquet Guest Ticket
|
$125.00 |
Hotel
Hilton Daytona Beach Oceanfront Resort
100 N. Atlantic Ave.
Daytona Beach, FL 32118
Use the above link to book your room within INSNA's rooming block. Reserve by May 25 to qualify for our exclusive room rate!
Room Rate: Guest rooms start at $199 USD/night.
Deadline to Reserve Room: May 25, 2026
NOTE: Should your room block show as sold out at any time, please select Book a Room on the landing page and then Edit Stay on the following page, to change the dates.
- Convenient conference access
- Self-parking discount: Guests in our room block receive a $15 USD discount on regular self-parking rates.
- Waived resort charge: The daily resort charge is waived for guests staying in our room block! Included with your stay at no additional charge:
- WiFi
- 1 hour beach bike and boogie board rental
- SpikeBall equipment
- $10 - $15 USD discount on food and beverage
- 15% discount at hotel spa and regular-priced gift shop apparel
- 1 kids arts & crafts activity
- 1 kids breakfast with purchase of adult buffet
Travel
There are three (3) airport options that serve Daytona Beach:
- Daytona Beach International Airport (DAB): located about 10 minutes from the host hotel; adjacent to Daytona International Speedway
- Orlando Sanford International Airport (SFB): located about 60 minutes from the host hotel
- Orlando International Airport (MCO): located 75 - 90 minutes from the host hotel
The Hilton Daytona Beach Oceanfront Resort does not provide a dedicated airport shuttle; however, multiple options are available for ground transportation to the host hotel:
- Rideshare services such as Uber or Lyft are available at airports with dedicated pick-up areas. Rates vary.
- Taxi services are available curbside at airports. Rates vary.
- Rental cars are available from multiple vendors at airports. Rates vary.
- Shuttle service is available from the SFB and MCO airports through GROOME Transportation. Please be sure to book early!
International Traveler Information
Foreign citizens traveling to the United States typically require a non-immigrant visa (commonly B-1 for business or B-2 for tourism) for temporary stays. Citizens from 41 countries in the Visa Waiver Program (WFP) can travel without a visa for up to ninety (90) days but must have an approved Electronic System for Travel Authorization (ESTA) before boarding. We encourage you to apply for visas and ESTA well in advance.
The INSNA team is happy to provide any registrants outside the United States with a visa letter! Just follow these steps:
- Register for Sunbelt: all registrants are required to designate in the registration form whether a visa letter is needed
- After registering, the INSNA team will send your visa letter to you via e-mail in a timely manner.
- If you need a visa letter more urgently, please contact the INSNA Office directly at support@insna.org to request your letter.
Helpful Links:
- General information on United States travel visas:
- Visa Waiver Program and ESTA Application
- Official ESTA Application
Note: In 2026, the United States government made changes to the list of countries that have travel restrictions to the United States. Please check the current information in all links provided.
If you are traveling internationally, consider avoiding entering the United States from major cities (e.g., New York, Los Angeles, Chicago, etc.) if possible. Immigration queues at large airports can be lengthy, increasing the risk of missing connection flights.
-
Some visitors traveling to the United States are required to have a passport that is valid for six (6) months beyond the period of their intended stay in the United States. Many countries are exempt from this rules - click here to verify whether this applies to you.
-
Ensure you have comprehensive medical insurance for your trip.
-
For entering the United States, ensure you have hard copies of hotel bookings and return tickets.
Learn More About Daytona Beach
See floor plans and amenities offered at the host hotel; learn about nearby attractions and restaurants; and earn discounts with the Show Your Badge program.
General Information
INSNA is currently accepting proposals for oral presentations and posters via Whova until Friday, March 13, 2026, 11:59 PM ET. Sunbelt presentations are grouped into Organized Sessions (in Whova they are called “tracks”). You are required to choose at least one (1)Track/Organized Session that fits your proposal best.
Click here to see the list of Track/Organized Session options!
How to Submit Proposals
Follow these steps to submit your proposal(s):
-
Go to the Call for Oral Presentations & Posters portal and click the Start proposal button.
-
You'll be prompted to create an account or log in. Enter your e-mail address and click the blue Continue button. Follow the prompts to either create your account or log in.
-
Complete the submission form.
-
Let us know if you'll be presenting in-person or virtually.
-
In the Submission Details section, select your main track(s) for your submission. Additional track options are available as well.
-
Designate whether you're submitting an oral presentation or a poster.
-
Include a title, summary, and 3 - 5 keywords that summarize your topic.
-
If you're presenting with additional people, please list them in the form.
-
-
Once you've completed the form, you can click the Save draft button if you need to come back and finish the form later, or you can click the Submit button to submit your proposal for review.
If you have any questions, please contact the INSNA Office at support@insna.org.
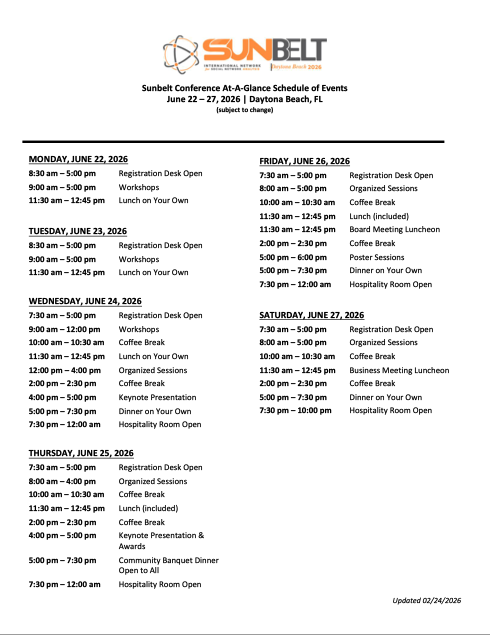
Sunbelt 2026 Schedule at a Glance*
*Subject to Change
Click on the Schedule at a Glance to download!
- Half-day workshops subject to schedule change as necessary
- Select title for full details, including co-presenters and workshop description.
- Registration for workshops will be available when registration opens for Sunbelt 2026.
- You must register for the main conference in order to register for in-person workshops.
Click the Pricing tab to learn more about workshop rates.
Monday Workshops - Full Day
This workshop is an introduction to the R programming language and its tools to represent, manipulate, and analyze egocentric or personal network data. Topics include: introduction to ego-network research and data; data structures and network objects in R; visualizing ego-networks; calculating measures on ego-network composition and structure; converting ego-network measures to R functions; applying these functions to many ego-networks. The workshop relies on R tidyverse packages for data science, showing how they can be used to conduct common operations in ego-network analysis and scale those operations up to large collections of networks. We'll cover specific packages for network analysis (igraph, network, egor), data management (dplyr) and programming (purrr). No previous familiarity with R is required; participants only need a laptop with R and RStudio installed. This workshop has been taught for the past several years at different international conferences, including INSNA's Sunbelt and EUSN meetings. It draws on concepts and methods from the instructor's forthcoming book "Analyzing personal networks using R" (SAGE, in press). More details on the workshop's materials and requirements are here: raffaelevacca.com/egonet-r.
Large Language Models, Text Embeddings, and Network Analysis - Ayan-Yue Gupta and Thomas Bryan Smith
This 6-hour session offers a practical introduction to Python and the synthesis of network analysis with natural language processing methods, including large language models (LLMs). This begins with an introduction to text data management and preprocessing in Python. We introduce embedding, discussing its development in the early 2010s and demonstrating practical applications. We start with word embeddings and word2vec, and the evolution from static word embeddings to contextual token embeddings through transformer architecture (e.g., BERT). Recent developments in post-ChatGPT generative LLMs, and how such developments (e.g. reinforcement learning from human feedback, contrastive learning) have improved text embedding generation, will be explored with LLM2Vec. The second half will guide attendees through the construction and analysis of networks derived of text embeddings. This will include topic modelling (BERT and LLM2Vec), and approaches to constructing network representations derived of topic embeddings – modelling the relational structure between the identified topics. The session will close with a demonstration of analyses which might be performed on the resulting network, such as backbone extraction (e.g., disparity filter, LANS) and the interpretation of the networks’ features.
Monday Workshops - Half-Day
What network selection mechanisms generate unique network structures and topologies? What are the implications of those selection mechanisms for individuals nested in social networks? This 3-hour workshop will introduce attendees to recent statistical frameworks for micro-macro network analysis using the netmediate package for R. The workshop will describe (1) procedures for estimating, interpreting, and null hypothesis testing the effects of micro-level selection mechanisms on macro-level network structures, and (2) introduce recent statistical procedures for evaluating the indirect effects of micro-level network selection mechanisms on individual and group level outcomes (e.g., adolescent smoking behavior). Topics covered will include (1) micro-macro analysis when the interest is treating a specific network structure (e.g., segregation, transitivity) as the dependent variable and (2) identification of indirect network selection effects on individual and group outcomes. We will review necessary assumptions for each type of analysis and strategies for meeting those assumptions in observational network data. Attendees will come away from the workshop with a deeper understanding of statistical procedures for micro-macro network analysis and how these procedures can be used to address research questions that implicate indirect network selection effects using netmediate.
The Internet serves as a vital platform for information access and global connectivity. Widespread online engagement offers unprecedented opportunities to study human behavior at scale, yet researchers face significant ethical and technical barriers when attempting to collect data for academic studies. Major social media platforms like Facebook and Twitter have progressively restricted access to their official Application Programming Interfaces (APIs), which previously served as primary tools for researchers to create customized datasets from specific platforms for studying online content production and engagement behavior. This workshop introduces the National Internet Observatory (NIO), an alternative data collection framework and infrastructure designed to help researchers study online behavior, with a particular focus on content viewing — the predominant form of online activity. The workshop presents NIO's informed data donation process, participant demographics and behavioral traces, and secure computing infrastructure. Further, the organizers will present concrete examples of research being conducted with this new source of data to motivate and inform workshop participants’ own ideas around the kind of research they can conduct with NIO. The workshop incorporates interactive activities and hands-on sessions with real aggregated data to demonstrate NIO's capabilities for enabling novel cross-disciplinary and cross-platform research across web and social media environments.
This workshop introduces a network-based approach to analysing the hardness and softness of scientific domains through their cognitive structure. Using Web of Science (WoS) data, participants will explore how network-derived indicators—such as centralities, clustering coefficients, entropy, and other structural measures—can describe whether a field is characterized by stable, cohesive, and centralized knowledge structures (hard science) or by diverse, fragmented, and flexible ones (soft science).
We shall first review the theory and evidence underlying this approach and then offer a practical demonstration of the methods involved. Using examples of workflows, we will extract key bibliometric features and construct cognitively meaningful co-reference networks from WoS records. Participants will apply Python and NetworkX to compute and interpret network measures that capture patterns of cohesion, integration, and diversity across disciplines.
By the end of the session, attendees will be able to retrieve and analyse network-based indicators that describe the cognitive and structural properties of scientific fields. The workshop will be particularly relevant for researchers in scientometrics, bibliometrics, and network science interested in applying quantitative network measures to study disciplinary structures and their cognitive organization.
Many sociological processes unfold as sequences of temporally ordered interaction events between entities. Leveraging the availability of time-stamped data, the Relational Event Model (REM) provides a powerful framework for generative modeling of such dynamic networks. REMs capture how node and edge characteristics, together with past interactions, shape the evolution of these processes. The essential temporal information embedded in relational event sequences has motivated advances in the specification of covariates and development of inference techniques.
In this workshop, we will introduce the foundations of REMs and show how to construct covariates that represent exogenous drivers, endogenous mechanisms, and temporal features of these processes. We will then examine likelihood-based inference methods for estimating covariate effects and discuss extensions that enhance the flexibility of REMs, including non-linear and time-varying influences as well as random effects to account for network and actor heterogeneity.
Workshop Agenda:
1. Core REMs: introduction to REM formulation and the inclusion of time-aware exogenous and endogenous variables.
2. REM inference: overview of likelihood-based estimation methods.
3. Non-Linear REMs: modeling non-linear and time-varying covariate effects while accounting for network and actor heterogeneity.
4. Practical Tutorial with R Studio: applying REMs to empirical datasets.
Prerequisites: Familiarity with R. Previous experience with the statnet packages network and sna is helpful but not required.
Synopsis:
This workshop will provide an introductory tutorial on using exponential-family random graph models (ERGMs) for statistical modeling of social networks, using a hands-on approach to fitting these models to data. The ERGM framework allows for the specification, estimation, and simulation of models that incorporate the complex dependencies within networks, and provides a general and flexible means of representing them. The session will demonstrate ERG modeling using the statnet software in R.
Topics covered within this session include: an overview of the ERGM framework; defining and fitting models to empirical data; interpretation of model coefficients; goodness-of-fit and model adequacy checking; simulation of networks using ERG models; degeneracy assessment and avoidance; and modeling and simulation of complete networks from egocentrically sampled data. Familiarity with basic descriptive network concepts and statistical methods for network analysis within the R/statnet platform is recommended. Attendees are expected to have had some prior exposure to R, but extensive experience is not assumed.
statnet is a collection of integrated packages for the R statistical computing environment that support the representation, manipulation, visualization, modeling, simulation, and analysis of network data. statnet is developed and maintained by a team of volunteer developers, and is released under the GNU Public License. statnet packages can be used with any computing platform that supports R (including Windows, Linux, and Mac). The software supports statistical analysis of large networks, temporal network analysis and valued ties, with utilities for missing and sampled data.The goal of this workshop is to provide participants an orientation to conducting personal networks research within Network Canvas and the opportunity to master the skills necessary to apply these tools within their specific domain of interest. Network Canvas (http://www.networkcanvas.com), is a free and open-source software suite that facilitates the collection of self-reported social network data, comprised of applications to support both in-person interviewer-assisted environments as well as remote self-administered studies.
In this workshop, we will provide an overview of Architect, the Network Canvas visual survey builder, as well as Interviewer, the Network Canvas app used to collect data directly from participants within an in-person research design. We will also provide an overview of Fresco, the newest Network Canvas tool designed for remote network surveying. Finally, we will explore data export in Interviewer and Fresco, and a brief orientation to analysis. Expect the opportunity to engage in hands-on exercises during the session with assistance from our team.
When completed, you will acquire the skills to:
- Design an egocentric or whole network survey
- Deploy and manage a study, whether in-person or remote
- Obtain study data in Interviewer and Fresco, and export it for analysis
This three-hour, hands-on workshop introduces participants to a suite of user-friendly tools, featuring the PLACE Plot platform and several open-source software tools, for developing and analyzing social network analysis (SNA) surveys for inter-organizational policy networks. Designed for researchers, evaluators, and policy practitioners, PLACEPlot streamlines the process of collecting high-quality relational data to map collaboration across agencies, organizations, and sectors.
The workshop begins with an overview of policy network analysis frameworks—emphasizing how SNA can illuminate patterns of collaboration, boundary spanning, and resource flow within complex policy systems. Participants will then explore PLACEPlot’s intuitive interface to design and deploy customized network surveys, manage respondent data, and generate real-time network visualizations without requiring advanced coding skills.
In the second segment, participants will learn how to connect survey outputs with RShiny applications for interactive reporting and stakeholder engagement. This portion highlights how to translate network data into meaningful visual narratives and dashboards that inform decision-making and drive collaboration.
By the end of the session, attendees will be able to (1) design and distribute SNA surveys using PLACEPlot, (2) interpret and visualize network data for policy insights, and (3) build interactive RShiny tools that make network findings accessible and actionable for diverse stakeholders.
Social network analysis has relied mainly on time-aggregated data and individual node connections. However, advances in data collection technologies now provide large amounts of time-stamped and hypernetwork information. Examples of such datasets include email multicast communication data and citation networks. Whereas methodological developments in temporal network science have expanded the toolkit for describing time-stamped and hypergraph data, relational hyper-event modeling has emerged as a central approach for the statistical modeling of the dynamic structures these data reveal. Recent contributions have made the Relational Hyper Event Model (RHEM) even more flexible, allowing it to address a range of applied demands.
In this workshop, we aim to present RHEMs, beginning with their core properties and progressing to their more novel modeling capacities, highlighting how they can be employed to address empirical questions.
Workshop Agenda:
- Core RHEMs: computing hyperevent covariates; formulating, estimating, and interpreting linear RHEMs.
- Non-Linear RHEMs: modeling non-linear, time-varying covariate effects while accounting for network and actor heterogeneity.
- Practical Tutorial with eventnet and R Studio: applying RHEMs to empirical datasets.
- Emerging Research Directions: exploring new questions and potential extensions for RHEMs.
Tuesday Workshops - Full Day
Socio-semantic network analysis (Basov and Roth, 2025; Basov et al., 2020; Roth and Cointet, 2010) explicitly links social structures (e.g., collaboration, advice, or friendship) and semantic structures (e.g., co-definitions or similarities between words, notions, or concepts). Such as an association between the terms ‘networks’ and ‘culture’ used by a pair of academics who are connected by a collaborative tie of co-editing. Ensembles of socio-semantic patterns are analysed to explain the – traditionally implicit and interpretively addressed – relation between social and cultural structures to formally grasp and model contextual meaning. For example, how the community of network analysis scholars understands its core terms, and how these understandings vary depending on themes, social ties and scholars’ attributes. This enables understanding explanations of how social ties shape perspectives, views, and ideas of actors - and vice versa.
Mixed-method socio-semantic network analysis training offered by this full-day hands-on workshop will introduce participants to: (1) computational word collocation approach, rooted in corpus linguistics, to produce semantic networks of associations between words; (2) descriptive network analysis of social, semantic, and socio-semantic structures; (3) interpretive analysis of texts—to understand these key elements in their textual and relational contexts; (4) basics of multilevel exponential random graph modelling as applied to socio-semantic structures.
The workshop is open to all participants, irrespective of their prior knowledge of descriptive network analysis or modelling. No programming skills are necessary. Participants are welcome to bring small training text datasets of their interest, along with text’s authors and matrices of social ties between them.
Tuesday Half-Day Workshops
Association football (soccer) is a model system for network science. From the history of sports analytics, scheduling of competitions, prediction of results, ranking of teams, analysis of matches, and scouting of players to the transfer market, business development, governance, media coverage, event tourism, and fan engagement, there are plenty of research opportunities that call for network approaches. The workshop is an introduction to the growing domain of soccer analytics. We provide an overview of problems and approaches, data and measurement, pitfalls and opportunities. In a companion workshop following this one, we provide in-depth descriptions of some novel network-analytic methods for match analysis.
Exponential random graph models (ERGM) are widely used in the social sciences to examine determinants of graph structure. This 3-hour workshop will introduce attendees to mediation and moderation analysis in ERGM using the ergMargins package for R. The workshop will describe why ERGM coefficients cannot be compared between models and why coefficients for interactions—including node matching, node mixing, and other common measures of homophily and heterophily—cannot be interpreted without adjustment. Topics covered will include (1) mediation analysis, (2) moderation analysis, (3) mediation analysis when the mediator is an interaction, and (4) mediation analysis when the main effect is an interaction. We will review a range of special cases, including interactions involving both continuous and discrete variables, necessary conditions for a causal interpretation, and mediation analysis involving endogenous graph statistics. Attendees will come away from the workshop with a deeper understanding of inferential difficulties in ERGM and with knowledge on how to address each issue using ergMargins.
Prerequisites: Some experience with R and familiarity with descriptive network concepts and statistical methods for network analysis in the R/statnet platform is expected. This workshop also assumes familiarity with ERGMs.
Synopsis:
This workshop will provide an introduction to modeling of network dynamics in continuous time using ERGM generating processes (EGPs). The exponential family random graph models (ERGMs) are a widely used framework for describing graph distributions, allowing flexible and parsimonious specification of both inhomogeneity (i.e., some ties are more likely than others) and dependence (i.e., some ties depend on others). EGPs complement ERGMs by providing ways of specifying continuous time dynamics whose long-run behavior recapitulates a specified ERGM distribution - thus allowing for dynamic network models that are consistent with specific cross-sectional behavior. In this session, we will begin with an overview of known classes of EGPs, with an eye to understanding the types of dynamic behavior embodied by each (and where they might be appropriate as empirical models). We will then discuss simulation and calibration of EGPs within the R/statnet platform, using the ergmgp package. We will show examples of the use of EGPs to generate dynamics consistent with cross-sectional network data combined with information on tie durations, including continuous time generalizations of the separable temporal ERGMs (STERGMs). Attendees are expected to have had some prior exposure to R and statnet, and completion of the statnet ERGM workshop session is strongly suggested as preparation for this session (as we will make extensive use of the ergm package).
statnet is a collection of packages for the R statistical computing system that supports the representation, manipulation, visualization, modeling, simulation, and analysis of relational data. statnet packages are contributed by a team of volunteer developers, and are made freely available under the GNU Public License. These packages are written for the R statistical computing environment, and can be used with any computing platform that supports R (including Windows, Linux, and Mac). statnet packages can be used to handle a wide range of simulation and analysis tasks, including support for large networks, statistical network models, network dynamics, and missing data.This workshop introduces the many ways that social networks influence individual and network-level behaviors. It also provides a brief introduction to analytic approaches for understanding network influences on behaviors; and reviews existing evidence for the utility of using social network data for behavior change in a variety of settings including health behaviors and organizational performance. A framework for using networks during program implementation is presented. The workshop also presents a typology of network interventions and reviews existing evidence on the effectiveness of network interventions. (Students familiar with the R environment may follow an R script written to demonstrate the 24 or so tactical interventions presented.) No software or computing requirements are needed. The workshop will be conducted by Tom Valente who has been developing and implementing network-based interventions for nearly 25 years.
The group stage of the FIFA World Cup 2026 concludes during Sunbelt, and there are going to be daily sessions with updates featuring match analyses, civilized discussions, and heated debates.
For those interested in the methods on which these analyses are based, we provide an introduction to some non-standard approaches employing proximity networks, affiliation networks, and passing networks to determine tactical elements such as dynamic player positioning. Many of them have been developed at ETH Zürich and may or may not be used by Team Switzerland.
For those interested, there will also be the opportunity for some hands-on exercises.
The aim of this workshop is to open up new perspectives that make watching world cup matches even more interesting, and more fun. In a companion workshop prior to this one, we provide additional background on soccer analytics more generally.
Prerequisites: Attendees are expected to have had some prior exposure to R, but extensive experience is not assumed. Familiarity with binary ERG modeling with the R/statnet platform (e.g., from the “Exponential Family Random Graph (ERGM) Modeling with statnet” workshop session) is assumed.
Synopsis:
This workshop session provides a tutorial using statnet software particularly ergm and latentnet to model social networks whose ties have weights (e.g., counts of interactions) or are ranks (i.e., each actor ranks the others according to some criterion), using latent space models and exponential-family random graph models (ERGMs) generalized to valued ties, and emphasizing a hands-on approach to fitting these models to empirical data.
The ERGM framework allows for the parametrization, fitting, and simulation from models that incorporate the complex dependencies within relational data structures, and provides an extremely general and flexible means of representing them, while latent space models postulate an unobserved social space in which actors are embedded, facilitating principled visualization and group detection. Topics covered within this session include: importing, modifying, and exporting edge values on network objects; an overview of the valued ERGM framework and the notion of reference distribution; an overview of latent space models for social networks; defining and fitting models to empirical data, including ERGM terms meaningful for counts and ranks; interpretation of model coefficients; simulation of networks using these models; and ERGM degeneracy assessment.
statnet is a collection of packages for the R statistical computing system that supports the representation, manipulation, visualization, modeling, simulation, and analysis of relational data. statnet packages are contributed by a team of volunteer developers, and are made freely available under the GNU Public License. These packages are written for the R statistical computing environment, and can be used with any computing platform that supports R (including Windows, Linux, and Mac). statnet packages can be used to handle a wide range of simulation and analysis tasks, including support for large networks, statistical networks, valued networks, network dynamics, and missing data.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is evolving at unprecedented speed, reshaping how we think, work, and collaborate. Once viewed primarily as a novel interface for interacting with computers, AI--especially with the rise of agentic systems and new model architectures--has become a powerful partner for researchers, educators, and practitioners across disciplines.
This workshop introduces participants to core concepts in AI literacy while showcasing emerging trends and practical tools that can enhance everyday academic and professional workflows. Designed for both newcomers and experienced users, the session will highlight how to use AI ethically, creatively, and productively--well beyond generating emails or simple text.
We will explore hands-on examples of leveraging AI for drafting and revising academic documents, supporting code development, and assisting with data analysis through agentic workflows. Participants will also learn about accessible online tools (such as ChatGPT and GitHub integrations) and programming-oriented options in R and Python, including local large language models through platforms like Ollama.
The workshop blends conceptual foundations with live demonstrations, giving attendees a clear overview of what AI can do today--and what the near future may bring. No prior experience with AI is required; curiosity and an interest in expanding your toolkit are all you need.
Wednesday Workshops - Half-Day
The netdiffuseR package provides tools for analyzing and simulating the diffusion of innovations and contagion processes on networks. In this workshop, we demonstrate the package’s features by analyzing empirical and simulated data on the diffusion of innovations. The session will include examples of using netdiffuseR jointly with other network analysis packages such as RSiena, statnet, and igraph. NetdiffuseR’s main features are computing network exposure models based on weight matrices (direct ties, structural equivalence, attribute-weighted, etc.), thresholds, infectiousness, and susceptibility. The package works with both static and dynamic networks. Some other capabilities include handling relatively large graphs, simulating networks and diffusion of innovation processes, and visualizing the diffusion of innovations.
While there are no prerequisites, it is suggested that you have a working knowledge of the R programming language. We will use the latest version of the netdiffuseR R package, which can be found on GitHub here: https://github.com/USCCANA/netdiffuseR. During the workshop day, we will provide access to a cloud version of RStudio with the latest version of netdiffuseR, so do not worry if you cannot install the package before the workshop.
Theoretical studies of opinion formation and evolution in social networks often focus on convergence to a set of steady-state opinions, namely asymptotic learning (with or without consensus). This is often motivated by the desire to seek an 'equilibrium' according to various definitions from statistical physics, control engineering, or economics. In many real social settings, however, it is observed empirically that opinions do not converge to a steady state; instead, they fluctuate indefinitely. This interdisciplinary workshop has three goals: (i) to introduce attendees to fundamental theoretical tools based on Bayesian inference that are suitable for modelling opinions and their evolution; (ii) to highlight some counter-intuitive yet realistic social phenomena that emerge when applying these tools; and (iii) to bring together practitioners from different knowledge domains (e.g. media studies, political science, education, artificial intelligence, social sciences, complex systems, and network sciences), who aspire to apply the tools to real-life systems. Specifically, we begin with an introduction to Bayesian statistics and belief propagation over networks. This enables us to learn the underlying tools required for modelling and analysis of opinion evolution across social networks. At this stage, we will also review some results on asymptotic learning on social networks facilitated by Bayesian inference. We then delve into a new model of opinion formation and evolution by enmeshing Bayesian learning and peer interactions. As an illustrative example, we consider a scenario where networked agents form beliefs about the political bias of a media organisation through consumption of media products, and peer pressure from political allies and opponents. To capture the multi-modal nature of opinions (individuals can hold contradictory beliefs with different levels of certainty), we model the agents' beliefs as probability distribution functions. In certain network structures, numerical simulations reveal counter-intuitive predictions, such as wrong conclusions being reached quicker with more certainty, turbulent non-convergence (some agents cannot “make up their mind” and vacillate in their beliefs), and intermittency (agents' beliefs flip between stable eras, where their beliefs do not vary over many time steps, and turbulent eras, where their beliefs fluctuate from one time step to the next). We will also consider belief disruption by partisans, i.e. stubborn agents who do not change their beliefs. If time permits, attendees will receive practical, hands-on instruction in coding the methods covered during the workshop.
This workshop provides a conceptual survey of the major streams of social network theory. Rather than teaching methods or software, it situates foundational network ideas within the broader landscape of social theory. Core mathematical constructs—such as centrality, structural equivalence, and core–periphery structure—are introduced only to clarify the theoretical debates they support, not for hands-on analysis. The workshop is aimed at participants who are new to the network perspective and want a clear map of the field’s main theoretical conversations.
The first part focuses on theories that treat network properties as drivers of outcomes. This includes classic work on social capital (weak ties, structural holes, social resources) and the contagion tradition (interpersonal influence, diffusion of innovation). We examine how centrality, cohesion, and related ideas are interpreted across these literatures, with attention to mechanisms, levels of analysis, and the role of social cognition in shaping perceived networks.
The second part turns to theories that explain the origins of network structure. Here the emphasis is on why networks take the forms they do and why actors come to occupy particular positions. Topics include homophily, preferential attachment, opportunities and constraints in choice, balance theory, and other mechanisms of tie formation.
By the end, participants will have a coherent framework for understanding how social scientists theorize about networks—both as causes of outcomes and as outcomes themselves—and how these lines of thought fit together in the broader social-scientific tradition.
In the interconnected and interdependent world of the twenty-first century, individual and collective outcomes — such as personal and public health, economic welfare, or war and peace — are affected by relationships among individual, corporate, state, and non-state actors. To understand how the world of the twenty-first century operates and make model-based predictions, it is vital to study networks of relationships and gain insight into how the structure of networks affects individual and collective outcomes. To study relationships among attributes under interference, a comprehensive regression framework for dependent predictors, outcomes, and connections is needed. We will provide workshop participants with a hands-on introduction to R package iglm, which implements a comprehensive regression framework for dependent predictors, treatments, outcomes, and connections with important advantages over existing approaches, including interpretability, scalability, and provable theoretical guarantees. We will demonstrate that R package iglm can be used to study spillover in connected populations, including hate speech on social media.
Fritz, C., Schweinberger, M., Bhadra, S., and D.R. Hunter (in press). A regression framework for studying relationships among attributes under network interference. Journal of the American Statistical Association.
A preprint is available at
https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/01621459.2025.2565851?src=exp-la
or
Purpose
Sunbelt 2026 is committed to providing an environment that is free of harassment of any kind for all the activities associated with it, whether in-person or online, including the informal components such as the conference dinner and the hospitality suite (hereafter, “Sunbelt 2026 activities”). Therefore, all INSNA members and other participants in Sunbelt 2026 activities, are expected to treat each other and service providers professionally and respectfully. The purpose of this code of conduct is to prevent harassment at Sunbelt 2026 activities and take immediate action should any harassment occur.
Unacceptable behaviors
Sunbelt 2026 will not tolerate any behavior generally known as offensive, demeaning, humiliating, intimidating, threatening, or verbally or physically aggressive, abusive, or disruptive. Unacceptable behaviors include:
- Epithets, ridicule, mockery, and slurs related to a person’s race, color, national or ethnic origin (ancestry), religion (creed), age, life and career stages, gender, gender expression, sexual orientation, physical or mental abilities or any other ground, or to characteristics related to grounds of discrimination such as a person’s dress or speech.
- Singling out a person for humiliating or demeaning “jokes” and insults, ridicule, name calling, bullying, and intimidation
- Unwelcome sexual attention
- Unwelcome physical contact and physical assaults
- Actual and implied veiled threats of harm
- Posting or circulating messages, pictures, or materials, whether in print or electronically, that is offensive or hostile toward an individual or group
- Sustained verbal or physical disruption of speakers or events
- Incitement of any of these or other unacceptable behaviors
- Retaliation against anyone who reports harassment or other unacceptable behaviors, assists another individual to report, or participates in an investigation of such a claim
Responsibilities
All members of INSNA and other participants in Sunbelt 2025 activities are expected to uphold and abide by this policy at Sunbelt 2026 by (1) not committing any form of harassment, (2) reporting any form of harassment experienced or witnessed to the staff leading Sunbelt 2026; and (3) cooperating fully in investigations of allegations of harassment.
In the case that harassment is reported, the Sunbelt 2026 Organizing committee will take immediate action to take appropriate measures that stop the offenders and help those experiencing harassment feel safe, for instance, by contacting local law enforcement or security or providing escorts. Reports of harassment will be kept confidential to the greatest extent feasible.
Any Sunbelt 2026 Organizers who have a significant conflict of interest will recuse themselves from overseeing this policy.
Consequences of misconduct
When harassment of any form is reported, members of the Sunbelt 2026 Organizing Committee will ask the offender(s) to stop their behaviour immediately and take the necessary legal steps, if applicable. It is at our discretion to expulse the offenders from the event without a refund. Incidents will also be reported to the INSNA president, and the INSNA board can vote to take further action.
Cancellation of registration must be made in writing to the INSNA Office at support@insna.org.
Refunds for Sunbelt 2026:
Conference and workshop fees due to cancellation will be processed as follows:
- Cancellation on or before May 1, 2026 at 11:59 PM ET - Refund 100% of registration fee, less a $25 processing fee.
- Cancellation between May 2 and May 18, 2026 at at 11:59 PM ET - Refund 50% of registration fee, less a $25 processing fee.
- Cancellation on or after May 19, 2026 - No refund due to cancellation
- Cancellation due to not receiving a Visa by time of travel - full refund less a $25 processing fee. Documentation required.
Workshops:
Changes to pre-conference workshop registrations may be considered as space permits.
For More Information:
INSNA Members qualify for discounted registration rates - renew your membership before registering to ensure you receive your discount!